Observed decline of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation 2004 to 2012
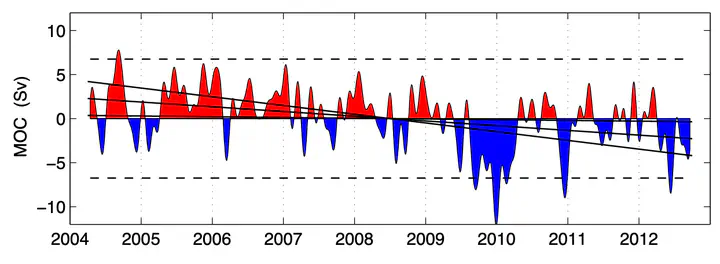 Anomalies (positive is northward) relative to mean annual cycle. A 45-day low-pass filter was applied to the time series. Horizontal dashed lines show ± 2 standard deviations and the solid black lines show the average trend ± 1.64 standard errors (i.e. 90 % confidence limits).
Anomalies (positive is northward) relative to mean annual cycle. A 45-day low-pass filter was applied to the time series. Horizontal dashed lines show ± 2 standard deviations and the solid black lines show the average trend ± 1.64 standard errors (i.e. 90 % confidence limits).Abstract
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) has been observed continuously at 26° N since April 2004. The AMOC and its component parts are monitored by combining a transatlantic array of moored instruments with submarine-cable-based measurements of the Gulf Stream and satellite derived Ekman transport. The time series has recently been extended to October 2012 and the results show a downward trend since 2004. From April 2008 to March 2012, the AMOC was an average of 2.7 Sv (1 Sv = 106 m3 s−1) weaker than in the first four years of observation (95% confidence that the reduction is 0.3 Sv or more). Ekman transport reduced by about 0.2 Sv and the Gulf Stream by 0.5 Sv but most of the change (2.0 Sv) is due to the mid-ocean geostrophic flow. The change of the mid-ocean geostrophic flow represents a strengthening of the southward flow above the thermocline. The increased southward flow of warm waters is balanced by a decrease in the southward flow of lower North Atlantic deep water below 3000 m. The transport of lower North Atlantic deep water slowed by 7% per year (95% confidence that the rate of slowing is greater than 2.5% per year).