Atmosphere drives observed interannual variability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation at 26.5N
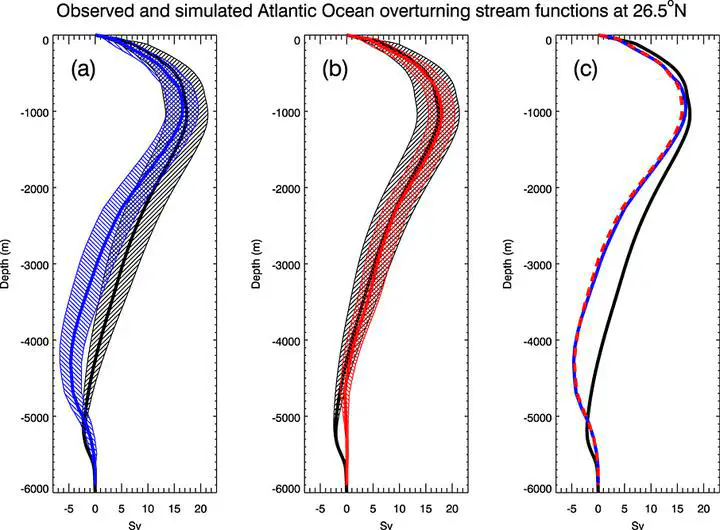 Time mean Atlantic meridional overturning stream functions at 26.5°N from RAPID (black in Figures 1a, 1b, and 1c) compared with overturning in ASSIM-3DVAR calculated using different methods: (a) Stream functions calculated using model velocities (blue). (b) Stream functions calculated using the RAPID-style method and a geostrophic reference depth of 4740 m (red). (c) Stream functions calculated using the RAPID-style method referenced to model velocities at 1000 m (dashed red line) compared with the mean profile (blue line) redrawn from Figure 1a. All calculations are for the period of January 2004 to December 2010, and hatching indicates a range of ±1 standard deviation calculated from monthly mean values.
Time mean Atlantic meridional overturning stream functions at 26.5°N from RAPID (black in Figures 1a, 1b, and 1c) compared with overturning in ASSIM-3DVAR calculated using different methods: (a) Stream functions calculated using model velocities (blue). (b) Stream functions calculated using the RAPID-style method and a geostrophic reference depth of 4740 m (red). (c) Stream functions calculated using the RAPID-style method referenced to model velocities at 1000 m (dashed red line) compared with the mean profile (blue line) redrawn from Figure 1a. All calculations are for the period of January 2004 to December 2010, and hatching indicates a range of ±1 standard deviation calculated from monthly mean values.Abstract
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) has been observed at 26.5°N since 2004. During 2009/2010, there was a transient 30% weakening of the AMOC driven by anomalies in geostrophic and Ekman transports. Here, we use simulations based on the Met Office Forecast Ocean Assimilation Model (FOAM) to diagnose the relative importance of atmospheric forcings and internal ocean dynamics in driving the anomalous geostrophic circulation of 2009/2010. Data-assimilating experiments with FOAM accurately reproduce the mean strength and depth of the AMOC at 26.5°N. In addition, agreement between simulated and observed stream functions in the deep ocean is improved when we calculate the AMOC using a method that approximates the observing array at 26.5°N. The main features of the geostrophic circulation anomaly are captured by an ensemble of simulations without data assimilation. These model results suggest that the atmosphere played a dominant role in driving recent interannual variability of the AMOC.