Major Variations in Sub-Tropical North Atlantic Heat Transport at Short (5 day) Timescales and their Causes
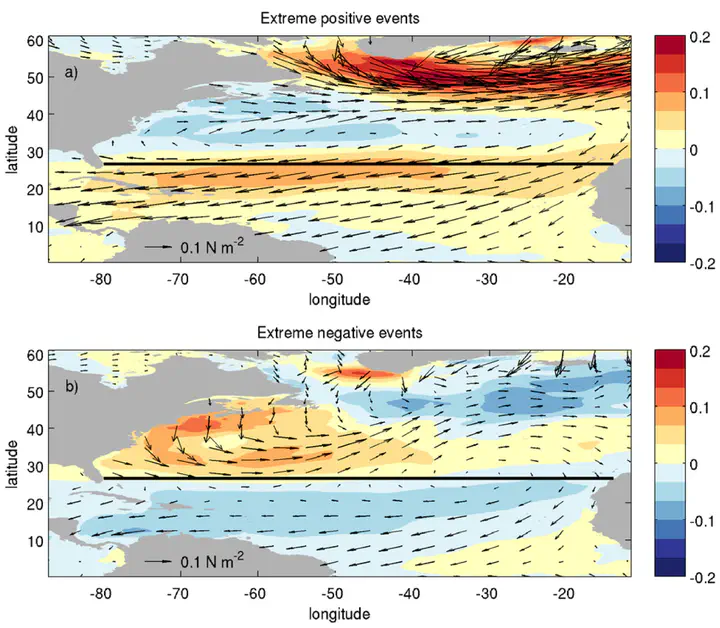 Model 5 day averaged wind stress anomaly (colored field) for (a) the 10 extreme positive events and (b) 10 extreme negative events between 1985 and 1994. The arrows show the mean wind stress averaged over the 10 events. The solid lines indicate the 26.58N latitude of the RAPID section.
Model 5 day averaged wind stress anomaly (colored field) for (a) the 10 extreme positive events and (b) 10 extreme negative events between 1985 and 1994. The arrows show the mean wind stress averaged over the 10 events. The solid lines indicate the 26.58N latitude of the RAPID section.Abstract
Variability in the North Atlantic ocean heat transport at 26.5°N on short (5 day) timescales is identified and contrasted with different behaviour at monthly intervals using a combination of RAPID/MOCHA/WBTS measurements and the NEMO-LIM2 1/12° ocean circulation/sea ice model. Wind forcing plays the leading role in establishing the heat transport variability through the Ekman transport response of the ocean and the associated driving atmospheric conditions vary significantly with timescale. We find that at 5 day timescales the largest changes in the heat transport across 26.5°N coincide with north-westerly airflows originating over the American land mass that drive strong southward anomalies in the Ekman flow. During these events the northward heat transport reduces by 0.5–1.4 PW. In contrast, the Ekman transport response at longer monthly timescales is smaller in magnitude (up to 0.5 PW) and consistent with expected variations in the leading mode of North Atlantic atmospheric variability, the North Atlantic Oscillation. The north-westerly airflow mechanism can have a prolonged influence beyond the central 5 day timescale and on occasion can reduce the accumulated winter ocean heat transport into the North Atlantic by ∼40%.