Measuring the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation at 26°N
Abstract
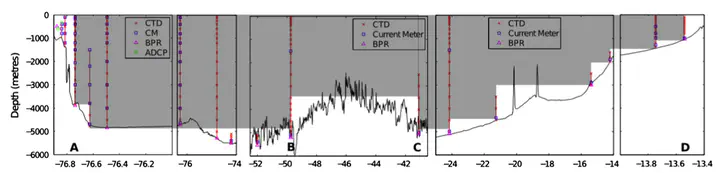
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) plays a key role in the global climate system through its redistribution of heat. Changes in the AMOC have been associated with large fluctuations in the earth’s climate in the past and projections of AMOC decline in the future due to climate change motivate the continuous monitoring of the circulation. Since 2004, the RAPID monitoring array has been providing continuous estimates of the AMOC and associated heat transport at 26°N in the North Atlantic. We describe how these measurements are made including the sampling strategy, the accuracies of parameters measured and the calculation of the AMOC. The strength of the AMOC and meridional heat transport are estimated as 17.2 Sv and 1.25 PW respectively from April 2004 to October 2012. The accuracy of ten day (annual) transports is 1.5 Sv (0.9 Sv). Improvements to the estimation of the transport above the shallowest instruments and deepest transports (including Antarctic Bottom Water), and the use of the new equation of state for seawater have reduced the estimated strength of the AMOC by 0.6 Sv relative to previous publications. As new basinwide AMOC monitoring projects begin in the South Atlantic and sub-polar North Atlantic, we present this thorough review of the methods and measurements of the original AMOC monitoring array.